Ganges River Countries On Its Course: A Comprehensive Exploration
The Ganges River, often regarded as the lifeline of India, is one of the most significant rivers in the world. Spanning across multiple countries, it plays a vital role in the lives of millions who depend on it for water, agriculture, and cultural practices. Known for its religious significance and ecological importance, understanding the countries along its course is essential for appreciating its global impact. In this article, we will delve into the countries through which the Ganges River flows, uncovering its rich history and relevance.
Beyond its geographical significance, the Ganges River is deeply intertwined with the cultural and spiritual fabric of South Asia. For centuries, it has been revered as a sacred river in Hinduism, drawing millions of pilgrims to its banks. This article aims to provide a detailed exploration of the countries on its course, shedding light on their unique relationships with the river.
As we explore the Ganges River countries on its course, we will examine the environmental, social, and economic implications of this mighty river. By understanding its journey through various nations, we can better appreciate the challenges and opportunities it presents to the regions it touches.
Read also:Understanding Chi940muepsilontau 941iotanutauzetaepsilonlambda Rho941iota Kappa940iotalambdaalpha A Comprehensive Guide
Table of Contents
- Geography of the Ganges River
- India: The Heart of the Ganges
- Nepal: The Origin of the Ganges
- Bangladesh: The Delta of the Ganges
- Ecological Significance
- Cultural Importance
- Economic Impact
- Challenges Facing the Ganges
- Solutions for Sustainable Management
- Future Prospects
Geography of the Ganges River
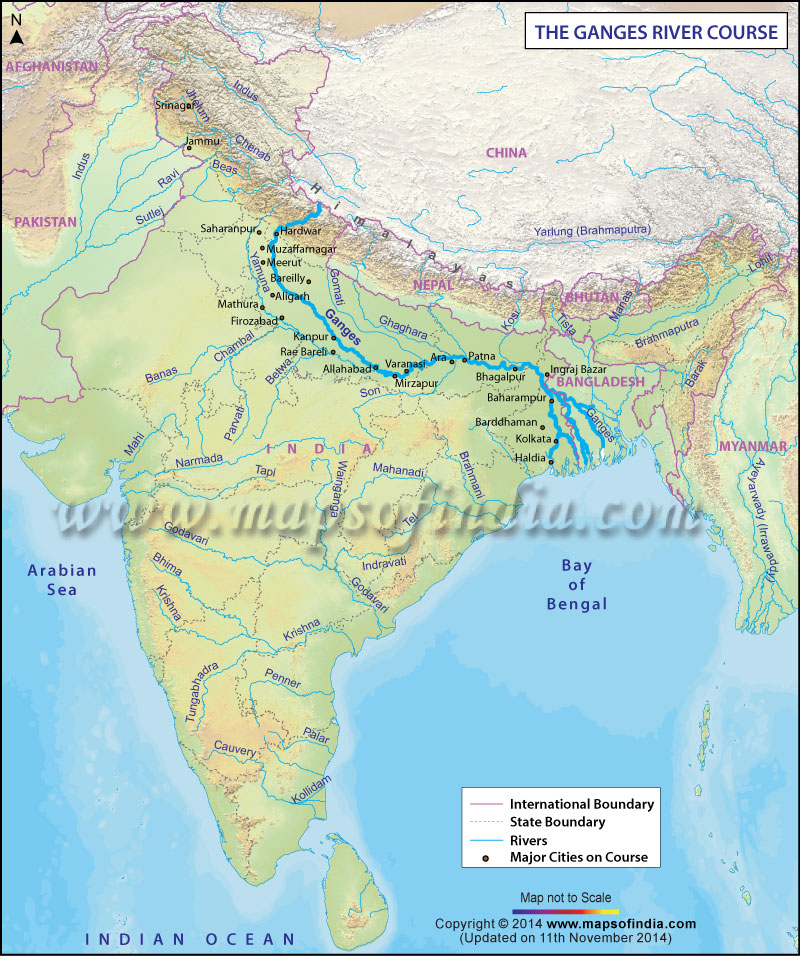
The Ganges River, stretching approximately 2,525 kilometers, originates in the Gangotri Glacier in the Indian Himalayas. It flows through the plains of North India before entering Bangladesh, where it merges with the Brahmaputra River to form the world's largest delta. The river's basin covers an area of about 1 million square kilometers, making it one of the most extensive river basins globally.
Key Countries on Its Course
- India
- Nepal
- Bangladesh
Each country plays a unique role in the river's journey, contributing to its ecological, cultural, and economic significance.
India: The Heart of the Ganges
India is the primary country through which the Ganges River flows. It is here that the river's cultural and religious importance is most evident. The Ganges is considered sacred by Hindus, who believe that bathing in its waters cleanses sins and aids in spiritual liberation.
Major Cities Along the Ganges in India
- Varanasi: A spiritual hub and one of the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world.
- Haridwar: Known for its Kumbh Mela, a massive Hindu pilgrimage.
- Kolkata: The river's mouth in India, where it begins its journey into Bangladesh.
India's dependence on the Ganges for agriculture, industry, and daily life underscores its importance in the country's development.
Nepal: The Origin of the Ganges
Nepal, although not directly traversed by the Ganges River, is home to its tributaries, such as the Kosi and Gandaki Rivers. These tributaries contribute significantly to the Ganges' flow, making Nepal an integral part of its ecosystem.
Environmental Impact
The Himalayan region, where the Ganges originates, is highly susceptible to climate change. Melting glaciers and changing precipitation patterns pose a threat to the river's sustainability. Nepal's role in conserving these vital water sources is crucial for the Ganges' future.
Read also:Girthmaster Vs Mia Z A Comprehensive Comparison
Bangladesh: The Delta of the Ganges
Bangladesh marks the end of the Ganges River's journey as it merges with the Bay of Bengal. The delta formed by the Ganges, Brahmaputra, and Meghna Rivers is the largest in the world, providing fertile land for agriculture and supporting a diverse ecosystem.
Economic Importance
The Ganges Delta is a lifeline for Bangladesh's economy, supporting industries such as fishing, agriculture, and shipping. However, it is also vulnerable to natural disasters like floods and cyclones, which pose significant challenges to the region's development.
Ecological Significance
The Ganges River supports a rich biodiversity, housing numerous species of fish, birds, and plants. It is home to endangered species such as the Ganges River Dolphin and the Indian Gharial. Protecting the river's ecosystem is vital for maintaining this biodiversity.
Threats to the Ecosystem
- Pollution from industrial waste and urban runoff
- Overfishing and habitat destruction
- Climate change and its impact on water flow
Efforts to conserve the Ganges' ecosystem involve international cooperation and sustainable practices.
Cultural Importance
Beyond its ecological significance, the Ganges River holds immense cultural value. It is central to Hindu rituals and traditions, with millions of devotees visiting its banks annually. The river's cultural importance extends beyond religion, influencing art, literature, and music.
Celebrations and Festivals
- Kumbh Mela: One of the largest religious gatherings in the world.
- Ganga Dussehra: A festival celebrating the descent of the Ganges to Earth.
These festivals highlight the river's role in uniting communities and fostering cultural heritage.
Economic Impact
The Ganges River plays a crucial role in the economies of India, Nepal, and Bangladesh. It supports agriculture, providing water for irrigation and fertile soil for crops. Additionally, it facilitates transportation and trade, connecting inland regions to coastal areas.
Challenges in Economic Development
Despite its economic benefits, the Ganges faces challenges such as water scarcity, pollution, and infrastructure development. Addressing these issues requires coordinated efforts among the countries it flows through.
Challenges Facing the Ganges
The Ganges River encounters numerous challenges that threaten its sustainability. Pollution, deforestation, and climate change are among the primary concerns. Industrial waste, untreated sewage, and agricultural runoff contribute significantly to the river's contamination.
International Efforts
Initiatives like the Namami Gange Programme in India aim to clean and rejuvenate the river. International organizations and governments are working together to implement sustainable practices and technologies to protect the Ganges.
Solutions for Sustainable Management
Sustainable management of the Ganges River requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes improving waste treatment infrastructure, promoting eco-friendly agricultural practices, and raising awareness about the river's importance.
Community Involvement
Engaging local communities in conservation efforts is essential for the river's long-term health. Programs that educate and empower communities can lead to more effective and sustainable outcomes.
Future Prospects
The future of the Ganges River depends on the actions taken today. By addressing the challenges it faces and implementing sustainable solutions, we can ensure its continued vitality for generations to come. Collaboration between countries and international organizations is key to achieving this goal.
Reference Sources:
- World Wildlife Fund (WWF)
- United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP)
- Government of India - Namami Gange Programme
Conclusion
The Ganges River countries on its course—India, Nepal, and Bangladesh—each play a vital role in the river's journey. From its spiritual significance in India to its ecological importance in Bangladesh, the Ganges is a lifeline for millions. Understanding the challenges it faces and working towards sustainable solutions is crucial for preserving this invaluable resource.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Explore other articles on our site to learn more about the world's fascinating rivers and ecosystems. Together, we can make a difference in protecting our planet's natural treasures.