Ganga River Flows Through Which Country: A Comprehensive Exploration
The Ganga River, one of the most sacred rivers in the world, flows through several countries in South Asia. It holds immense cultural, religious, and economic significance for millions of people. Understanding its journey across different nations is crucial for appreciating its role in the region's history and geography.
As one of the major rivers in the Indian subcontinent, the Ganga River has been a lifeline for civilizations that have thrived along its banks for thousands of years. From its source in the Himalayas to its delta in the Bay of Bengal, the river spans vast distances and crosses multiple borders, making it a fascinating subject for exploration.
In this article, we will delve into the countries through which the Ganga River flows, its geographical significance, and the cultural importance it holds. Whether you're a geography enthusiast, a traveler, or simply curious about this mighty river, this article will provide you with all the information you need.
Read also:Comprehensive Remoteiot Device Management Tutorial For Beginners
Table of Contents
- Geographical Overview of the Ganga River
- Countries Through Which Ganga Flows
- India and the Ganga River
- Bangladesh and the Ganga River
- Nepal and the Ganga River
- Cultural Significance of the Ganga River
- Environmental Challenges Faced by the Ganga
- Conservation Efforts for the Ganga River
- Statistics and Facts About the Ganga River
- Conclusion
Geographical Overview of the Ganga River
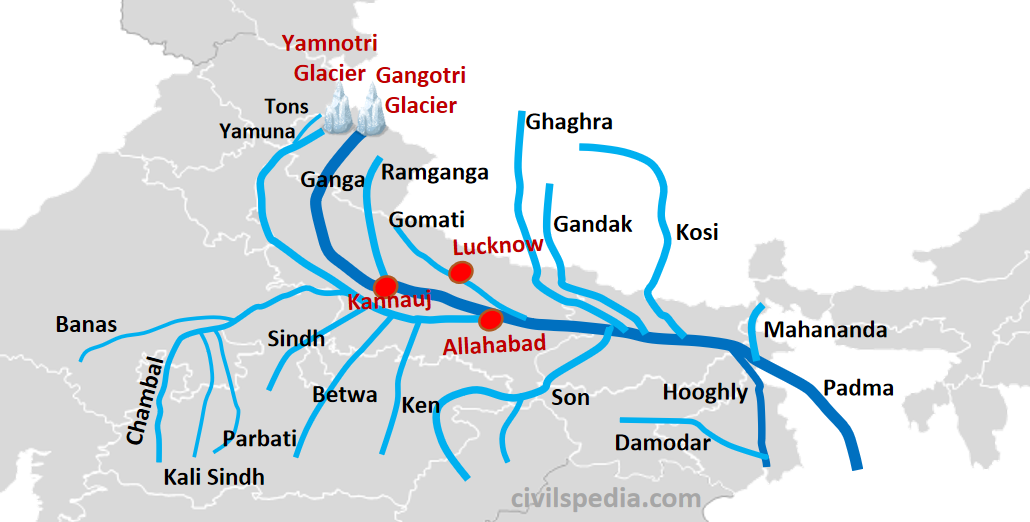
The Ganga River, often referred to as the Ganges, is one of the longest rivers in Asia, stretching approximately 2,525 kilometers (1,569 miles). Its journey begins in the Gangotri Glacier in the Indian Himalayas and flows through the plains of North India before emptying into the Bay of Bengal. The river forms a crucial part of the Indo-Gangetic Plain, which is one of the most fertile regions in the world.
Geographically, the Ganga River plays a vital role in shaping the landscape of South Asia. Its basin covers an area of about 1,080,000 square kilometers, providing water for agriculture, industry, and millions of people living along its banks.
The river's course is divided into three main sections: the upper course in the Himalayas, the middle course through the plains of North India, and the lower course in the delta region. Each section has its unique characteristics and contributes to the river's overall significance.
Major Tributaries of the Ganga River
- Yamuna River
- Ghaghara River
- Gandak River
- Kosi River
- Brahmaputra River (in Bangladesh)
Countries Through Which Ganga Flows
The Ganga River primarily flows through three countries: India, Bangladesh, and Nepal. Each country has a unique relationship with the river, which influences its cultural, economic, and environmental dynamics.
India: The Heart of the Ganga's Journey
India is the primary country through which the Ganga River flows. It covers the majority of the river's course, from its origin in the Himalayas to its entry into Bangladesh. The river is considered sacred by Hindus and is worshipped as the goddess Ganga.
Bangladesh: The Delta Region
In Bangladesh, the Ganga River is known as the Padma River. It merges with the Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers to form the world's largest delta, the Sundarbans. This delta region is crucial for the country's agriculture and biodiversity.
Read also:Mastering Remoteiot Vpc Ssh On Windows 10 A Comprehensive Guide
Nepal: The Upper Reaches
Although the Ganga River does not originate in Nepal, several of its tributaries, such as the Kosi and Gandak, originate in the country. These tributaries contribute significantly to the river's flow and connect Nepal to the broader Ganga Basin.
India and the Ganga River
In India, the Ganga River holds immense importance, both culturally and economically. The river is considered the lifeblood of the country, supporting millions of people who depend on it for their livelihoods.
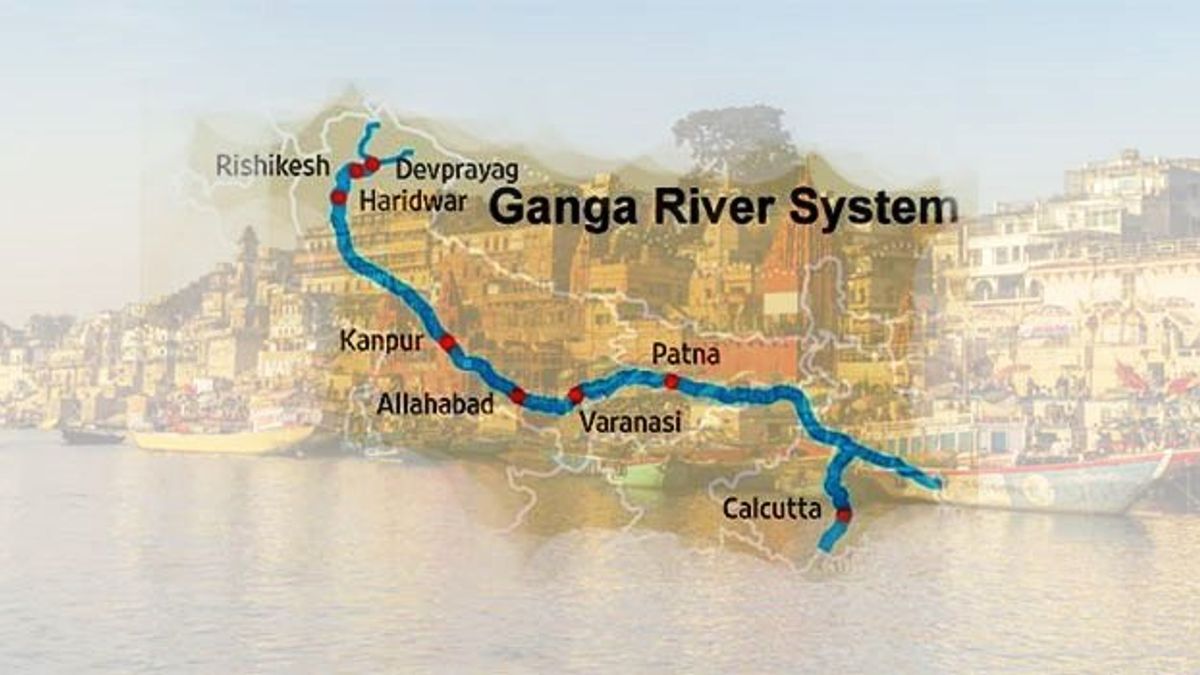
Religious Significance: The Ganga River is worshipped as a goddess by Hindus and is believed to have purifying powers. Pilgrims from all over the world visit sacred sites along the river, such as Varanasi, Allahabad (Prayagraj), and Haridwar, to perform rituals and seek blessings.
Economic Importance: The river supports agriculture, fishing, and transportation. The fertile plains irrigated by the Ganga River are some of the most productive agricultural regions in the world.
Major Cities Along the Ganga River
- Haridwar
- Varanasi
- Kanpur
- Patna
- Kolkata
Bangladesh and the Ganga River
In Bangladesh, the Ganga River is known as the Padma River. It plays a crucial role in the country's economy and environment, particularly in the delta region.
Environmental Importance: The Sundarbans, the world's largest mangrove forest, is located in the delta region formed by the Ganga, Brahmaputra, and Meghna rivers. This region is home to diverse flora and fauna, including the Bengal tiger.
Economic Contribution: The Padma River supports agriculture, fishing, and transportation in Bangladesh. It provides water for irrigation and serves as a vital transportation route for goods and people.
Challenges in Bangladesh
Bangladesh faces several challenges related to the Ganga River, including flooding, erosion, and pollution. These challenges require coordinated efforts between India and Bangladesh to ensure the sustainable management of the river.
Nepal and the Ganga River
Nepal contributes to the Ganga River through its tributaries, such as the Kosi and Gandak rivers. These tributaries originate in the Himalayas and flow into India, where they merge with the main stem of the Ganga River.
Hydropower Potential: Nepal has significant hydropower potential due to its location in the Himalayas. The Kosi and Gandak rivers are being developed for hydropower projects to meet the country's energy needs.
Environmental Concerns: Nepal faces challenges such as deforestation and soil erosion, which can affect the flow of its rivers. Sustainable management practices are essential to ensure the long-term health of the Ganga Basin.
Cultural Significance of the Ganga River
The Ganga River is deeply intertwined with the cultural and spiritual life of South Asia. It is considered sacred by Hindus and is believed to have divine origins. The river is mentioned in ancient texts such as the Vedas and the Puranas, highlighting its importance in Hindu mythology.
Festivals and Rituals: Several festivals and rituals are associated with the Ganga River, including the Kumbh Mela, which is one of the largest religious gatherings in the world. Pilgrims from all over the world visit the river to perform rituals and seek blessings.
Art and Literature: The Ganga River has inspired countless works of art, literature, and music. It is a symbol of purity, renewal, and spiritual awakening in Indian culture.
Environmental Challenges Faced by the Ganga
Despite its cultural and economic significance, the Ganga River faces numerous environmental challenges that threaten its health and sustainability.
Pollution: Industrial waste, sewage, and agricultural runoff are major sources of pollution in the Ganga River. This pollution affects the water quality and poses health risks to people and wildlife.
Deforestation: Deforestation in the Himalayas has led to increased soil erosion, which affects the river's flow and contributes to flooding.
Climate Change: Climate change is affecting the Himalayan glaciers, which are the source of the Ganga River. Melting glaciers and changing precipitation patterns could have long-term impacts on the river's flow.
Solutions to Environmental Challenges
- Implementing stricter pollution control measures
- Promoting sustainable agriculture practices
- Restoring forest cover in the Himalayas
- Encouraging community participation in river conservation
Conservation Efforts for the Ganga River
Efforts to conserve the Ganga River have been ongoing for several decades, with various initiatives aimed at addressing its environmental challenges.
Government Initiatives: The Indian government has launched several programs, such as the Namami Gange Project, to clean and rejuvenate the Ganga River. These programs focus on pollution control, afforestation, and community engagement.
NGO and Community Efforts: Several NGOs and community groups are working to protect the Ganga River through awareness campaigns, river clean-up drives, and advocacy for sustainable practices.
International Cooperation: India, Bangladesh, and Nepal are collaborating on initiatives to manage the Ganga Basin sustainably. This cooperation is essential for addressing transboundary issues such as flooding and pollution.
Statistics and Facts About the Ganga River
Here are some interesting statistics and facts about the Ganga River:
- The Ganga River is the third largest river in the world by discharge volume.
- It provides water to over 40% of India's population.
- The Ganga Basin covers an area of about 1,080,000 square kilometers.
- The river supports over 500 species of fish and 90 species of amphibians.
- The Sundarbans, formed by the Ganga River, is a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
Conclusion
The Ganga River flows through India, Bangladesh, and Nepal, making it a vital resource for millions of people in South Asia. Its cultural, economic, and environmental significance cannot be overstated. However, the river faces numerous challenges, including pollution, deforestation, and climate change, which require urgent attention.
Efforts to conserve the Ganga River are ongoing, with governments, NGOs, and communities working together to address its challenges. By promoting sustainable practices and raising awareness, we can ensure the long-term health and sustainability of this mighty river.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences about the Ganga River in the comments below. If you found this article informative, please consider sharing it with others. For more articles on geography, culture, and the environment, explore our website further.